On July 25, 2025, the South Pacific region was rattled by a powerful yet deep-seated 6.6 magnitude earthquake, striking southwest of Samoa, a remote island nation known for its pristine beaches and vibrant Polynesian culture. While the quake did not result in any reported casualties or infrastructure damage, it drew international attention due to its strength and depth, and reignited conversations about tectonic activity along the notorious Pacific Ring of Fire.
In this article, we break down the full story behind this seismic event — including what happened, why it matters, and what scientists are saying about it.
📍 Epicenter and Depth: Where Did It Happen?
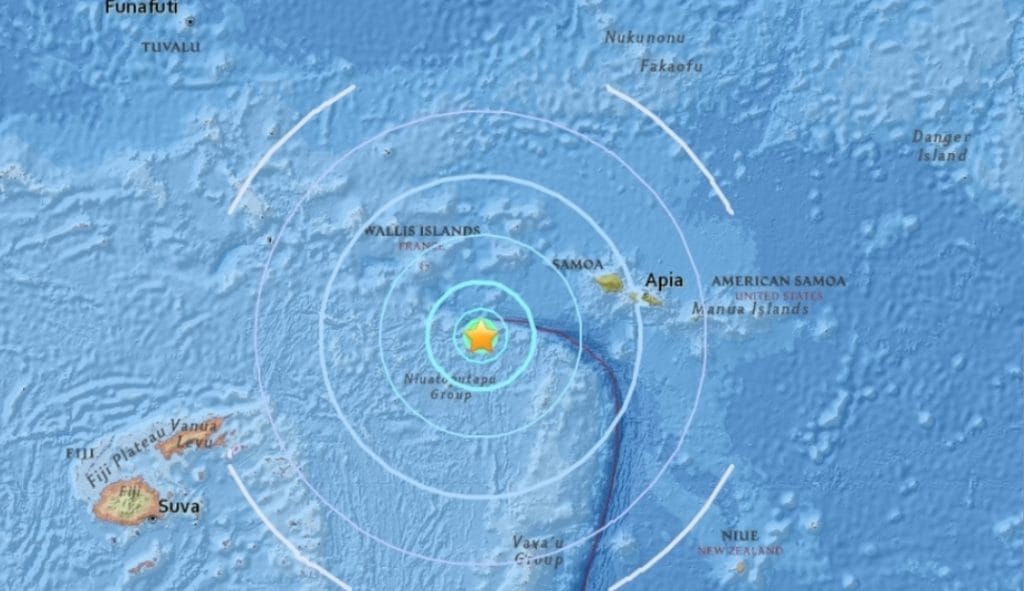
According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the earthquake struck approximately 440 kilometers (273 miles) southwest of Apia, Samoa’s capital city. The quake’s depth was recorded at around 112 kilometers (70 miles) beneath the earth’s surface, which classifies it as an intermediate-depth earthquake.
Intermediate-depth quakes typically originate between 70 km and 300 km beneath the surface. While they tend to cause less surface-level destruction than shallower earthquakes, they can still be felt across wide regions due to the way seismic waves travel through the earth’s crust and mantle.
Despite the quake’s magnitude, its depth helped mitigate any surface-level shaking, and no tsunami warnings were issued.
🌐 No Tsunami Threat, No Casualties
Following standard protocol, tsunami monitoring centers, including the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center, quickly analyzed the seismic data. They confirmed that the earthquake did not generate any tsunami threats to Samoa or surrounding nations.
Local government agencies in Samoa and nearby territories issued public safety statements to reassure citizens. Fortunately, no damage, injuries, or disruptions to public utilities were reported in the hours after the quake.
Residents of Samoa and American Samoa, accustomed to living in an earthquake-prone region, reported light shaking in some areas, but most said they were unaware the earthquake had occurred until news alerts went out.
🔥 Ring of Fire: A Tectonic Hotspot
The location of this earthquake is no surprise to geologists. Samoa sits along the Pacific Ring of Fire — a 40,000-kilometer horseshoe-shaped zone where over 75% of the world’s active and dormant volcanoes are located. This region is also responsible for about 90% of the world’s earthquakes.
The Ring of Fire is formed by subduction zones, where tectonic plates collide, and one plate is forced beneath another. These tectonic battles occur miles below the surface, releasing enormous amounts of energy when pressure finally gives way — resulting in earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or both.
The July 25 quake was a result of this subduction activity, likely involving the interaction between the Pacific Plate and the Australian Plate.
⛑ Earthquake Preparedness in Samoa
Earthquakes are not new to the Samoan islands. The most devastating in recent memory was the 2009 Samoa earthquake and tsunami, a magnitude 8.1 quake that generated a tsunami killing over 180 people and displacing thousands.
Since then, the Samoan government has invested in:
- Early warning systems
- Public education campaigns
- Emergency preparedness drills
- Better infrastructure planning
This recent earthquake was a reminder of the importance of these efforts. It also served as a stress test of emergency protocols, communication systems, and the public’s responsiveness to alerts.
Local officials used the event to reinforce disaster awareness, urging citizens to review their emergency plans and stay informed through official channels.
🧠 What Do Scientists Say?
Seismologists and geologists around the world are carefully analyzing data from the Samoa quake. While it is part of the expected tectonic activity in the region, every earthquake helps researchers:
- Refine earthquake prediction models
- Understand deep-earth stress distributions
- Track plate motion and interactions
The USGS and regional institutions like Geoscience Australia and GNS Science in New Zealand have noted that the quake’s depth and moderate energy release make it an important event for study, especially in terms of how energy dissipates in oceanic subduction zones.
They have also confirmed that this quake does not appear to be a foreshock or part of a larger swarm, although continuous monitoring is ongoing.
🛫 Travel and Tourism: No Impact Reported
Samoa, known for its peaceful islands, lush rainforests, and vibrant marine life, is a growing tourism destination. Following the earthquake, the Samoa Tourism Authority confirmed that:
- All airports remained operational.
- No hotels or resorts reported damage.
- Tour schedules continued without interruption.
Travel advisories from neighboring countries, including Australia and New Zealand, did not issue any restrictions related to the earthquake. The event was seen as a geological occurrence rather than a threat to public life or the tourism industry.
💬 Reactions From the Region
In Samoa, public reaction was mostly calm. Many citizens said they didn’t feel anything and only learned about the quake through social media or news apps. Others used the opportunity to share preparedness tips or retell stories from past earthquakes.
American Samoa, Tonga, and Fiji also reported no impact from the tremor. Their disaster agencies monitored the situation but issued no alerts, citing the depth and distance from population centers.
On X (formerly Twitter), hashtags like #SamoaEarthquake and #RingOfFire trended regionally, with users sharing maps, safety messages, and updates from USGS and Pacific Tsunami Warning Center.
🌎 Why This Matters Globally
Even though this particular earthquake caused no direct harm, it underscores the persistent and unpredictable nature of tectonic activity. It’s a reminder that preparedness is crucial — not just for Pacific nations but for any region near fault lines.
For global scientists and emergency response teams, every significant earthquake is a data point that helps:
- Improve response systems
- Upgrade infrastructure design
- Advance earthquake early warning technology
It also raises awareness about the fragility of island nations, many of which face dual threats from tectonic activity and rising sea levels.
📌 Key Takeaways
- A magnitude 6.6 earthquake struck near Samoa on July 25, 2025.
- It occurred 440 km southwest of Apia, at a depth of 112 km.
- No tsunami, no casualties, and no damages were reported.
- It was caused by subduction activity in the Pacific Ring of Fire.
- Authorities used the event to promote disaster preparedness.
- Seismologists are analyzing it to enhance global understanding of earthquakes.
🧭 Final Thoughts
While the recent quake near Samoa did not bring devastation, it was a clear signal from the earth’s inner forces — a reminder that nature is always shifting beneath our feet. For Samoa and its Pacific neighbors, resilience is not just about reacting to disasters but staying prepared before they strike.
As island nations continue to navigate a changing climate and restless geology, events like these serve not only as geological footnotes but as catalysts for policy, education, and community strength.
Let this be a gentle tremor that shakes us awake — not in fear, but in preparation.